Spay
Spaying your pet entails surgical removal of the reproductive organs. In females, these are the ovaries and uterus, and the procedure is called an ovariohysterectomy, or spay. For routine spaying, the best age for dogs and cats is before puberty. Spaying is considered a routine abdominal operation. Spaying reduces risk of certain illnesses, such as pyometra (a common, life-threatening infection of the uterus) or mammary gland cancer.

Neuter
"Neuter" is a common term for castration in a dog. It is the surgical removal of a male dog's testicles. A neuter must be performed under general anesthesia by a licensed veterinarian. A neuter is sometimes referred to as getting the dog "fixed." Neutering your male companion prevents testicular cancer and some prostate problems. Your neutered male may be better behaved. Unneutered dogs and cats are more likely to mark their territory by spraying strong-smelling urine all over the house. Your dog might be less likely to mount other dogs, people and inanimate objects after he’s neutered. Some aggression problems may be avoided by early neutering.
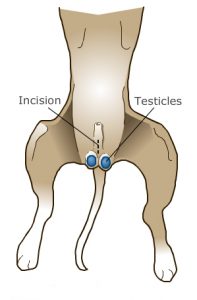
(Spaying and Neutering your pet reduces pet overpopulation. Millions of dogs are put down every year because there aren’t enough homes for them. Spaying your pet before her first heat offers the best protection from these diseases. neutering your pet decreased roaming: A behavioral advantage of neutering is that these dogs will not 'roam' when they sense a female in heat.)